Introduction

Caffeine is one of the most widely consumed psychoactive substances in the world. Found naturally in coffee, tea, and various plants, it is renowned for its ability to increase alertness and combat fatigue. According to the FDA, about 80% of U.S. adults consume caffeine daily. Its popularity stems from its effectiveness as a central nervous system stimulant, which can enhance cognitive and physical performance.
In addition to natural sources, caffeine is available in supplement form. These supplements come in various forms, including pills, powders, and energy drinks, and offer a convenient way to consume controlled doses of caffeine. Unlike a cup of coffee, which can vary in caffeine content, supplements provide a precise amount of caffeine, making it easier to manage intake.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to caffeine supplements. It will explore their benefits, risks, and best practices for safe use. Additionally, it will offer insights into choosing the right supplement and discuss natural alternatives. By the end of this guide, readers will have a well-rounded understanding of how caffeine supplements can fit into their lifestyle and how to use them responsibly. Learn more from Medical News Today.
What Are Caffeine Supplements?
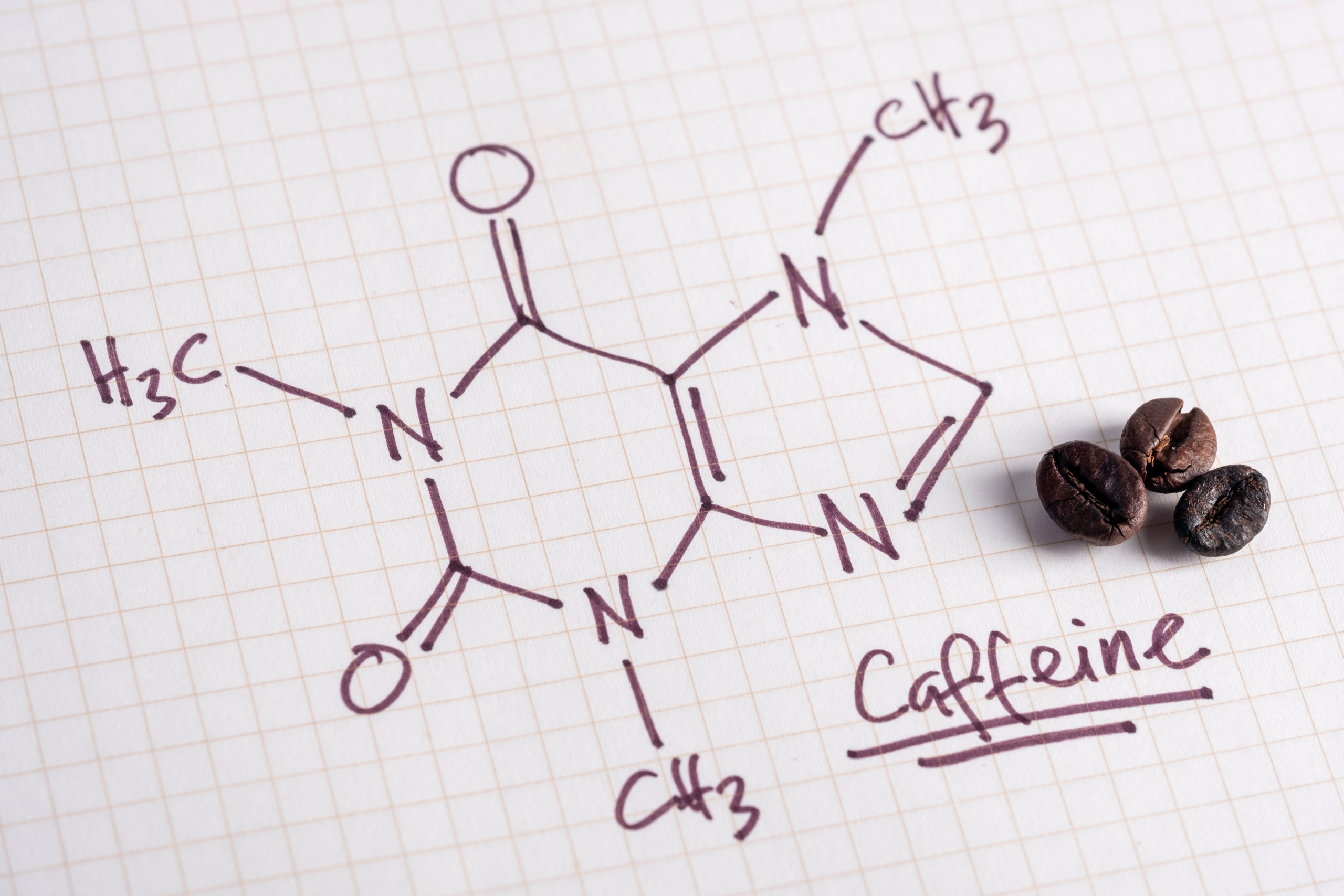
Caffeine supplements are products designed to provide a concentrated dose of caffeine. These supplements come in various forms, including:
- Pills: Often used for their convenience and precise dosage, caffeine pills are a popular choice among those looking to avoid the calories and sugars in energy drinks.
- Powders: These can be mixed with water or other beverages, allowing for customizable doses.
- Energy Drinks: These beverages typically contain caffeine along with other ingredients like taurine, vitamins, and sugars to enhance energy and alertness.
Natural sources of caffeine include coffee, tea, and certain plants like guarana and yerba mate. While these sources provide additional health benefits, such as antioxidants and other nutrients, their caffeine content can vary significantly. For example, a typical cup of coffee contains 95 mg of caffeine, but this can vary based on the type of coffee and brewing method. In contrast, caffeine supplements offer a consistent and predictable dose, making it easier to manage intake. Read more about caffeine’s effects on the WebMD.
Caffeine supplements often contain additional ingredients to enhance their effects or provide additional benefits. Common additives include:
- Taurine: An amino acid that can improve mental performance when combined with caffeine.
- B Vitamins: These vitamins help convert food into energy and are commonly added to energy drinks.
- L-Theanine: Often found in tea, this compound can help mitigate some of the jittery effects of caffeine, promoting a more relaxed state of alertness.
Benefits of Caffeine Supplements

Caffeine supplements offer a range of benefits, making them popular among athletes, students, and busy professionals alike. These benefits extend across physical performance, cognitive function, and weight management. Find out on Council for Responsible Nutrition.
Enhanced Physical Performance
Caffeine is well-known for its ability to enhance physical performance. It stimulates the central nervous system, leading to increased adrenaline production. This hormone prepares the body for intense physical activity, resulting in improved endurance and strength. Numerous studies have shown that caffeine can significantly improve performance in endurance sports like running and cycling by reducing perceived effort and delaying fatigue.
Improved Endurance and Strength
Caffeine supplements are particularly effective in improving endurance and strength. By mobilizing fatty acids from fat tissues and making them available for energy production, caffeine helps preserve glycogen stores in muscles. This can prolong the time to exhaustion, allowing athletes to perform longer and more intensely. Research has shown that athletes taking caffeine supplements can experience a 2-4% improvement in endurance and strength performance.
Fatigue Reduction
One of the primary reasons people turn to caffeine is for its ability to combat fatigue. Caffeine works by blocking the action of adenosine, a neurotransmitter that promotes sleep and relaxation. This blockage leads to increased neuronal firing and the release of other neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine, which help maintain alertness and reduce the perception of fatigue.
Cognitive Benefits
Beyond physical performance, caffeine supplements also offer significant cognitive benefits.
Increased Alertness and Concentration: Caffeine is widely used to enhance alertness and concentration. It stimulates the brain, leading to improved focus and mental clarity. This is especially beneficial for tasks that require sustained attention and vigilance, such as studying or working on complex projects.
Improved Memory and Cognitive Function: Studies have shown that caffeine can improve various aspects of cognitive function, including memory. For example, a study found that caffeine can enhance memory consolidation, making it easier to retain new information. Additionally, caffeine has been shown to improve reaction times and other aspects of executive function.
Weight Management
Caffeine supplements can also play a role in weight management.
Appetite Suppression: Caffeine has appetite-suppressing properties, which can help reduce calorie intake. This effect can be particularly useful for those looking to lose weight or manage their appetite during fasting periods.
Increased Metabolism: Caffeine can increase metabolic rate, helping the body burn more calories even at rest. It stimulates thermogenesis, the process by which the body generates heat and energy from digesting food. This can lead to increased calorie expenditure and, over time, weight loss.
Risks and Side Effects
While caffeine supplements offer numerous benefits, they also come with potential risks and side effects. Understanding these can help users make informed decisions and use caffeine responsibly.
Common Side Effects
Caffeine supplements can cause a range of side effects, especially when taken in high doses or by individuals sensitive to caffeine.
- Jitters: One of the most common side effects is the feeling of jitteriness or nervousness. This can be particularly pronounced in individuals who are not regular caffeine users.
- Anxiety: High doses of caffeine can increase anxiety levels. This is because caffeine stimulates the release of adrenaline, which can lead to a heightened sense of alertness and, in some cases, anxiety.
- Insomnia: Due to its stimulating effects, caffeine can interfere with sleep patterns. Consuming caffeine late in the day can lead to difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, resulting in insomnia.
Potential Health Risks
In addition to common side effects, caffeine supplements can pose more serious health risks, particularly when consumed in large amounts or over extended periods. Check out this guide on caffeine myths and facts.
- Heart Issues: High doses of caffeine can increase heart rate and blood pressure, potentially leading to cardiovascular problems. Individuals with pre-existing heart conditions should be particularly cautious when using caffeine supplements.
- Dependency: Regular use of caffeine can lead to physical dependence. Symptoms of caffeine withdrawal, such as headaches, fatigue, and irritability, can occur when a habitual user reduces or stops their intake.
- Digestive Issues: Caffeine can increase stomach acid production, leading to digestive discomfort, acid reflux, or exacerbation of ulcers.
Interaction with Other Medications and Health Conditions
Caffeine can interact with various medications and exacerbate certain health conditions.
- Medications: Caffeine can interact with certain medications, altering their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. For example, caffeine can interfere with the absorption and effectiveness of medications like lithium, used for bipolar disorder, and some antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin.
- Health Conditions: Individuals with certain health conditions should be cautious with caffeine intake. People with anxiety disorders, heart conditions, gastrointestinal issues, and sleep disorders may find their symptoms worsened by caffeine.
Best Practices for Safe Use
Using caffeine supplements responsibly involves understanding the appropriate dosages, timing, and strategies to minimize side effects. Specific populations, such as athletes and students, can benefit from tailored guidelines to maximize the benefits while minimizing risks.
Recommended Dosages and Timing
The amount of caffeine that is safe and effective can vary widely among individuals. However, general guidelines can help ensure safe consumption.
- Dosages: The FDA suggests that up to 400 milligrams (mg) of caffeine per day is generally safe for most adults. This is roughly equivalent to four cups of brewed coffee. For caffeine supplements, it’s important to follow the manufacturer’s dosage recommendations and start with the lowest effective dose to assess tolerance.
- Timing: To avoid sleep disturbances, it’s advisable to consume caffeine supplements earlier in the day. Consuming caffeine 6 hours or more before bedtime can help reduce the risk of insomnia. For athletes, timing caffeine intake around 30-60 minutes before exercise can optimize performance benefits.
Tips for Minimizing Side Effects
Minimizing the potential side effects of caffeine supplements involves careful management of intake and monitoring the body’s response.
- Gradual Increase: For those new to caffeine supplements, gradually increasing the dose can help the body adapt and reduce the likelihood of adverse effects like jitters and anxiety.
- Hydration: Caffeine has diuretic properties, so it’s important to stay well-hydrated to counteract potential dehydration. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is essential.
- Balanced Diet: Consuming caffeine supplements with a balanced diet can help mitigate digestive issues. Avoid taking caffeine on an empty stomach to reduce the risk of stomach upset or acid reflux.
Guidelines for Specific Populations
Different groups may have specific needs and considerations when using caffeine supplements.
- Athletes: Athletes can benefit from caffeine’s performance-enhancing effects, but it’s crucial to follow sport-specific guidelines and consider the timing and dosage carefully. Some sports organizations have regulations on caffeine use, so athletes should ensure compliance.
- Students: Students often use caffeine to enhance focus and concentration. To avoid dependency and sleep disturbances, students should limit caffeine intake to early in the day and use it strategically, such as before studying or exams. Maintaining a balanced study schedule and incorporating natural breaks can also help sustain cognitive performance without over-reliance on caffeine.
- Older Adults: Older adults may be more sensitive to caffeine’s effects and should start with lower doses. Monitoring blood pressure and cardiovascular health is particularly important in this group.
How to Choose the Right Caffeine Supplement

Selecting the appropriate caffeine supplement involves considering various factors to ensure safe and effective caffeine consumption. Understanding these factors, along with careful review of product labels and certifications, can help users make informed decisions. Additionally, knowing which brands are reputable can provide confidence in the quality and safety of the supplements.
Factors to Consider
When choosing a caffeine supplement, several key factors should be taken into account to match the product with individual needs and preferences.
- Dosage: One of the most critical aspects of caffeine supplementation is the dosage. The recommended dosage can vary based on individual tolerance, health conditions, and specific needs. For general use, a moderate dose of 100-200 mg per serving is common. For athletic performance, doses of 3-6 mg per kilogram of body weight are often used to achieve ergogenic effects. Always start with the lowest effective dose to assess tolerance.
- Form: Caffeine supplements come in various forms, including pills, powders, capsules, and energy drinks. Each form has its advantages:
- Pills/Capsules: These provide a convenient and precise way to control caffeine ingestion.
- Powders: These allow for customizable dosages and can be mixed with beverages.
- Energy Drinks: These often combine caffeine with other ingredients to enhance energy and alertness, but may also contain high levels of sugar and artificial additives.
- Additional Ingredients: Many caffeine supplements include other ingredients to enhance their effects or provide additional benefits. Common additives include:
- L-Theanine: Found in tea, this amino acid can help smooth out the jittery effects of caffeine and promote a more focused, calm alertness.
- B Vitamins: These are often added to support energy metabolism and overall vitality.
- Herbal Extracts: Ingredients like guarana or green tea extract can provide additional antioxidants and synergistic effects.
Reviewing Product Labels and Certifications
Careful review of product labels and certifications is essential to ensure the safety and efficacy of caffeine supplements.
- Labels: A detailed examination of the product label can provide critical information about the caffeine content, serving size, and additional ingredients. Look for transparency in labeling, where all active and inactive ingredients are clearly listed. The label should also include information on the recommended dosage and any potential warnings or contraindications.
- Certifications: Third-party certifications can provide an added layer of assurance regarding the quality and safety of the supplement. Certifications from organizations like NSF International, USP (United States Pharmacopeia), or Informed-Sport indicate that the product has been tested for purity and potency and is free from banned substances. These certifications can be particularly important for athletes who need to ensure compliance with anti-doping regulations.
Recommendations for Reputable Brands
Choosing supplements from reputable brands can significantly reduce the risk of consuming low-quality or contaminated products. Here are some brands known for their quality and transparency:
- NOW Foods: Known for its commitment to quality and extensive range of supplements, NOW Foods offers several caffeine products that are well-regarded for their purity and efficacy.
- Optimum Nutrition: This brand is popular among athletes and fitness enthusiasts for its high-quality sports nutrition products, including caffeine pills and energy blends. Their products are often tested for banned substances, making them a safe choice for competitive athletes.
- Kaged Muscle: Another top choice for athletes, Kaged Muscle provides third-party tested caffeine supplements that are free from artificial colors and flavors. Their focus on clean, effective ingredients has earned them a strong reputation.
Alternatives to Caffeine Supplements
While caffeine supplements offer convenience and precision in caffeine consumption, there are several alternatives that can provide similar benefits. These alternatives include natural sources of caffeine, other stimulants and cognitive enhancers, and lifestyle changes aimed at promoting sustained energy levels.
Natural Sources of Caffeine
Natural sources of caffeine can offer additional health benefits beyond the stimulant effects, thanks to the presence of other beneficial compounds.
- Coffee: Perhaps the most popular natural source of caffeine, coffee is rich in antioxidants and has been linked to numerous health benefits, including reduced risks of certain diseases. A typical cup of brewed coffee contains about 95 mg of caffeine.
- Tea: Tea, particularly green and black varieties, contains lower amounts of caffeine compared to coffee but also provides a wealth of antioxidants and other bioactive compounds. Green tea, in particular, is rich in L-theanine, which can promote a state of calm alertness and enhance cognitive function. Black tea typically contains about 47 mg of caffeine per cup, while green tea contains around 28 mg.
- Yerba Mate: This traditional South American beverage is made from the leaves of the Ilex paraguariensis plant and provides a caffeine boost along with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. A typical serving of yerba mate contains about 85 mg of caffeine.
- Guarana: A plant native to the Amazon, guarana seeds contain about twice the caffeine concentration of coffee beans. It is often used in energy drinks and natural supplements for its stimulant effects.
Other Stimulants and Cognitive Enhancers
Aside from caffeine, there are other stimulants and cognitive enhancers that can help improve focus, alertness, and energy levels.
- L-Theanine: This amino acid, found naturally in tea leaves, is often combined with caffeine to enhance cognitive performance without the jittery side effects. It promotes relaxation while maintaining alertness, making it an ideal complement to caffeine.
- Rhodiola Rosea: An adaptogenic herb that can help reduce fatigue and improve mental performance under stress. It’s often used to enhance energy and endurance.
- Ginseng: Used for centuries in traditional medicine, ginseng is believed to enhance physical and mental performance, reduce fatigue, and improve overall well-being.
Lifestyle Changes for Sustained Energy
In addition to supplements and natural sources, lifestyle changes can play a significant role in maintaining high energy levels and cognitive performance throughout the day.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity boosts overall energy levels and can improve mood and cognitive function. Even moderate exercise, like walking or yoga, can help sustain energy.
- Balanced Diet: Eating a diet rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, provides the necessary nutrients for sustained energy. Avoiding excessive sugar and processed foods can help prevent energy crashes.
- Adequate Sleep: Prioritizing sleep is crucial for maintaining energy and cognitive performance. Adults typically need 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Practices like maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a restful environment, and limiting caffeine intake in the late afternoon can promote better sleep.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is essential for optimal bodily functions and energy levels. Even mild dehydration can impair cognitive function and physical performance.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can deplete energy and impact mental health. Techniques like mindfulness, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress and maintain energy levels.
