Introduction
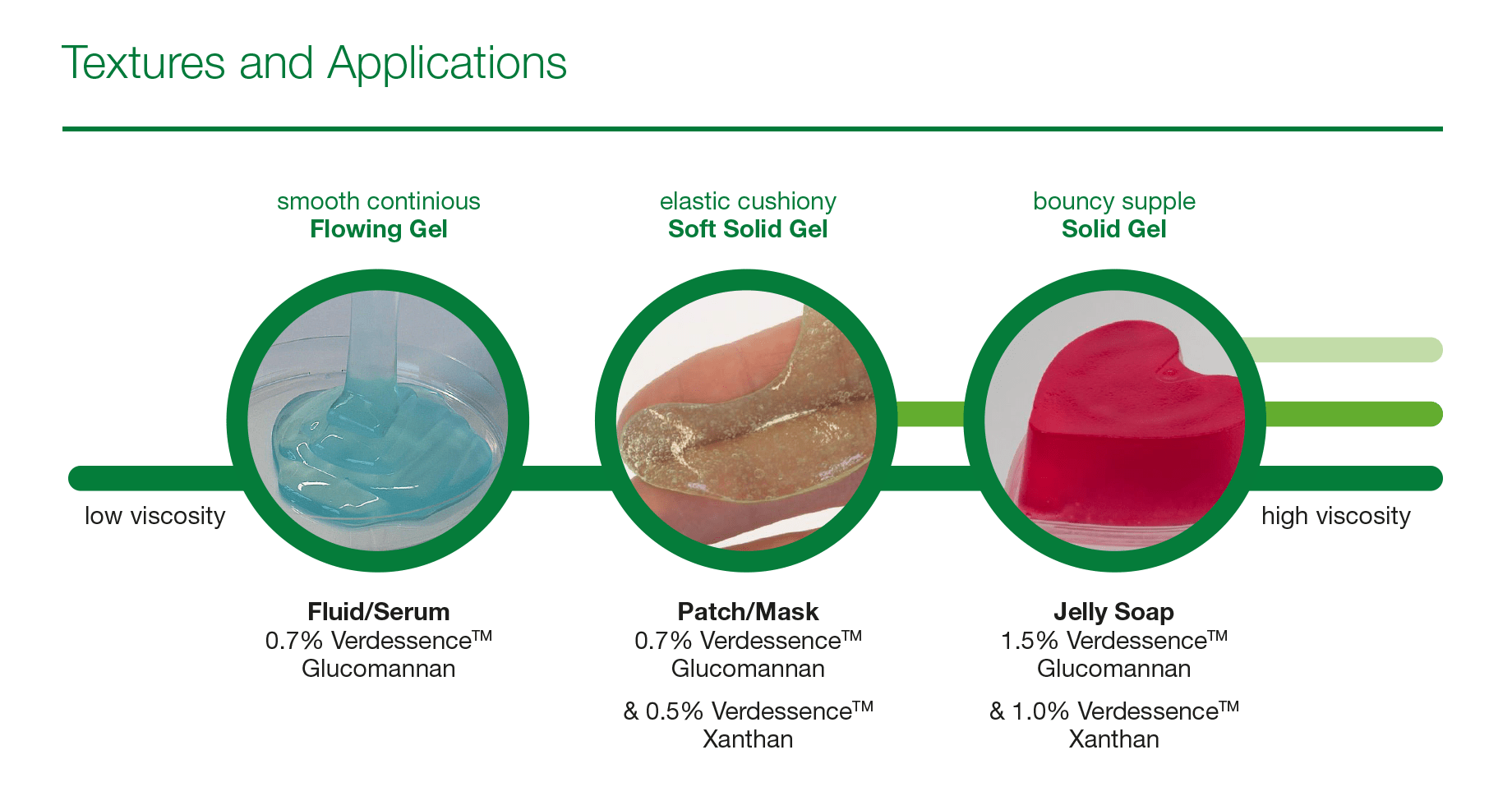
Brief Overview of Glucomannan
Glucomannan is a natural, water-soluble dietary fiber extracted from the roots of the konjac plant (Amorphophallus konjac). Known for its high viscosity and exceptional ability to absorb water, glucomannan has been used for centuries in traditional Asian cuisines and medicines. When consumed, it forms a gel-like substance in the stomach, which can help to slow down digestion and provide a feeling of fullness. This unique property makes glucomannan a popular ingredient in various weight loss supplements and dietary products. More information can be found on Healthline.
Importance and Relevance of Glucomannan in Health and Nutrition
The significance of glucomannan in health and nutrition cannot be overstated. Due to its high fiber content, glucomannan plays a crucial role in promoting digestive health and regularity. Its ability to expand and create a sense of satiety can aid in weight management by reducing overall calorie intake. Additionally, glucomannan has been shown to help lower cholesterol levels and regulate blood sugar, making it beneficial for individuals with cardiovascular conditions and diabetes. For more details, you can refer to WebMD.
What is Glucomannan?
Definition and Origin
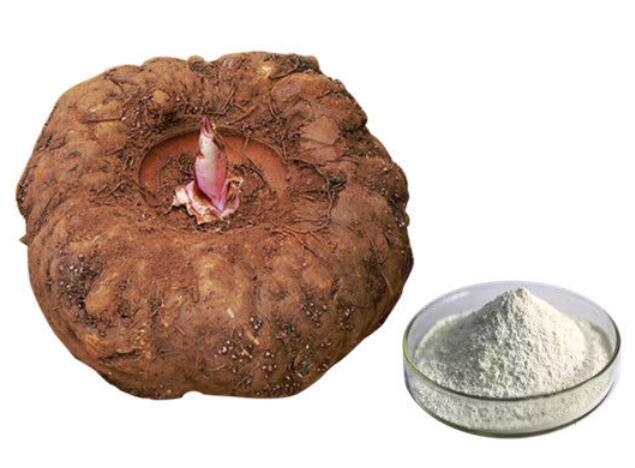
Glucomannan is a naturally occurring, water-soluble dietary fiber. It is primarily derived from the root of the konjac plant, scientifically known as Amorphophallus konjac. The konjac plant is native to Asia, particularly found in regions such as Japan, China, and Southeast Asia. Historically, glucomannan has been used in traditional Asian cuisine and herbal medicine for its health benefits and culinary versatility.
Source: Konjac Plant
The konjac plant, also known as elephant yam or konnyaku, is the primary source of glucomannan. The plant’s tuberous root contains high concentrations of this unique fiber. The roots are harvested, cleaned, and processed to extract glucomannan. This extracted glucomannan is then used to create various forms, such as powders, capsules, tablets, and food products like konjac noodles and gel-based foods. More information can be found on NCBI.
Chemical Composition and Properties
Glucomannan is composed of long chains of glucose and mannose, two types of simple sugars, linked together by beta-1,4-glycosidic bonds. This structure gives glucomannan its high molecular weight and remarkable water-absorbing properties. When mixed with water, glucomannan can absorb up to 50 times its weight, forming a viscous, gel-like substance. This gel-like consistency is what enables glucomannan to slow down digestion, promote a feeling of fullness, and support various health benefits such as weight management, cholesterol reduction, and blood sugar regulation.
Health Benefits of Glucomannan
Weight Loss and Appetite Control
One of the most well-known benefits of glucomannan is its ability to aid in weight loss and appetite control. Due to its high fiber content, glucomannan expands in the stomach when it absorbs water, forming a gel-like substance. This expansion increases the feeling of fullness, which can help reduce overall calorie intake by curbing hunger and controlling appetite. Several studies have shown that glucomannan supplementation can contribute to modest weight loss when combined with a balanced diet and regular exercise. A detailed study can be found on NCBI.
Cholesterol Management
Glucomannan has been shown to help lower cholesterol levels, particularly low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol. It achieves this by binding to bile acids in the gut, which are then excreted from the body. To produce more bile acids, the liver uses cholesterol from the blood, thereby lowering overall cholesterol levels. Regular consumption of glucomannan can thus contribute to improved heart health and a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Blood Sugar Regulation
For individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition, glucomannan can be beneficial in regulating blood sugar levels. The gel-like fiber slows down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, leading to a more gradual rise in blood sugar levels after meals. This can help prevent spikes in blood glucose and improve overall glycemic control. Incorporating glucomannan into the diet can be a useful strategy for managing diabetes and maintaining stable blood sugar levels. More information is available on RxList.
Digestive Health and Constipation Relief
Glucomannan’s high fiber content is also beneficial for digestive health. As a soluble fiber, it helps to soften stools and promote regular bowel movements, making it an effective remedy for constipation. By increasing stool bulk and stimulating peristalsis, glucomannan supports overall digestive function and can alleviate symptoms of gastrointestinal discomfort. Additionally, its prebiotic properties nourish beneficial gut bacteria, further enhancing digestive health.
Potential Benefits for Gut Microbiome
Emerging research suggests that glucomannan may have positive effects on the gut microbiome. As a prebiotic fiber, it serves as a food source for beneficial bacteria in the gut, promoting their growth and activity. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for various aspects of health, including immune function, nutrient absorption, and inflammation regulation. By supporting the growth of good bacteria, glucomannan can contribute to a balanced and thriving gut microbiome, which in turn supports overall health and well-being. For further reading, see NCBI.
Uses of Glucomannan

Dietary Supplements
Glucomannan is widely used in dietary supplements due to its health benefits, particularly for weight management, cholesterol reduction, and blood sugar control. These supplements typically come in the form of capsules, tablets, or powders. When taken before meals with water, glucomannan supplements can help promote a feeling of fullness, reducing overall calorie intake and supporting weight loss efforts. Additionally, they can be used to support digestive health and manage blood sugar levels as part of a comprehensive health regimen.
Food Additives
Glucomannan is commonly used as a food additive due to its thickening and stabilizing properties. In particular, it is a key ingredient in konjac noodles, also known as shirataki noodles. These low-calorie, low-carbohydrate noodles are popular in various diets, including ketogenic and low-carb diets, for their ability to provide satiety without adding significant calories.
Functional Foods
Glucomannan is increasingly incorporated into functional foods designed to provide additional health benefits beyond basic nutrition. These foods are formulated to improve health and well-being, often targeting specific conditions like obesity, high cholesterol, and diabetes. Examples of functional foods containing glucomannan include fortified snacks, meal replacement shakes, and health bars. These products leverage glucomannan’s properties to enhance satiety, improve digestion, and support metabolic health, making them convenient options for health-conscious consumers.
Medicinal Uses in Traditional Practices
In traditional Asian medicine, glucomannan has been used for centuries for its therapeutic properties. It has been utilized to treat various ailments, including digestive disorders, skin conditions, and inflammatory diseases. Traditional practitioners often recommend glucomannan for its detoxifying properties, believing that it helps cleanse the body of toxins and impurities. Moreover, its soothing effect on the digestive system makes it a natural remedy for constipation and gastrointestinal discomfort. While modern research continues to explore and validate these traditional uses, glucomannan remains a staple in many holistic health practices, valued for its natural healing properties and overall health benefits.
How to Use Glucomannan

Recommended Dosages for Various Purposes
The appropriate dosage of glucomannan can vary depending on the specific health goal:
- Weight Loss: Studies suggest that a typical dose for weight loss is about 1 gram of glucomannan, taken three times a day with water before meals.
- Cholesterol Management: A common dosage for lowering cholesterol levels is 3 to 4 grams per day, divided into multiple doses.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: To help manage blood sugar levels, a daily intake of 3 grams, divided into smaller doses before meals, is often recommended.
- Digestive Health: For alleviating constipation, 1 to 2 grams of glucomannan taken with plenty of water can help promote regular bowel movements and improve digestive function.
Forms Available: Powder, Capsules, Tablets, Food Products
Glucomannan is available in various forms to suit different preferences and needs:
- Powder: Glucomannan powder can be mixed with water, smoothies, or other beverages. It’s versatile and easy to incorporate into various recipes.
- Capsules and Tablets: These are convenient options for those who prefer pre-measured doses. They are easy to take with water, especially before meals.
- Food Products: Glucomannan is also found in specific food products, such as konjac noodles (shirataki noodles) and konjac-based snacks. These products integrate glucomannan into everyday meals seamlessly.
Tips for Incorporating Glucomannan into Daily Diet
To effectively incorporate glucomannan into your daily routine, consider the following tips:
- Start Slow: Begin with a lower dose to allow your body to adjust to the increased fiber intake, and gradually increase the dosage.
- Stay Hydrated: Always take glucomannan with plenty of water to prevent choking and ensure it expands properly in the stomach. Drink at least 8 ounces of water with each dose.
- Integrate into Meals: Add glucomannan powder to your morning smoothie or sprinkle it into soups and stews. Konjac mannan, found in shirataki noodles, can be used as a low-calorie substitute for traditional pasta.
- Consistency is Key: For weight loss and cholesterol management, consistency is essential. Regularly take glucomannan before meals to maximize its benefits.
- Experiment with Recipes: Use glucomannan in baking to add fiber to your breads and pastries. Its thickening properties can also improve the texture of gluten-free recipes.
Safety and Side Effects
Possible Side Effects and How to Mitigate Them
While glucomannan is generally considered safe for most people, it can cause some side effects, particularly if taken in large amounts or without adequate water:
- Digestive Issues: Some people may experience bloating, gas, diarrhea, or stomach cramps. To mitigate these effects, start with a lower dose and gradually increase it to allow your digestive system to adjust.
- Choking Hazard: If not taken with enough water, glucomannan can expand before reaching the stomach, posing a choking hazard or causing blockages in the throat or esophagus. Always take glucomannan with plenty of water (at least 8 ounces) to ensure it reaches the stomach safely.
- Allergic Reactions: Though rare, some individuals may have allergic reactions to glucomannan. Symptoms may include itching, rash, or difficulty breathing. Discontinue use and seek medical attention if you experience any signs of an allergic reaction.
Precautions and Contraindications
Certain individuals should take precautions or avoid using glucomannan altogether:
- Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women: There is limited research on the safety of glucomannan for pregnant or breastfeeding women. It is advisable to consult a healthcare provider before use.
- People with Gastrointestinal Conditions: Those with existing gastrointestinal disorders, such as Crohn’s disease, colitis, or any form of bowel obstruction, should avoid glucomannan as it may exacerbate their conditions.
- Children: Due to the risk of choking, glucomannan supplements are generally not recommended for young children. Consult a pediatrician before giving glucomannan to children.
Interactions with Medications
Glucomannan can interact with certain medications, affecting their efficacy or absorption:
- Diabetes Medications: Since glucomannan can lower blood sugar levels, it may enhance the effects of diabetes medications, potentially leading to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Monitor blood sugar levels closely and consult your healthcare provider to adjust medication dosages if necessary.
- Cholesterol-Lowering Drugs: Glucomannan may enhance the cholesterol-lowering effects of medications such as statins. While this can be beneficial, it’s important to monitor cholesterol levels and adjust medications under medical supervision.
- Oral Medications: Due to its ability to slow down digestion, glucomannan may affect the absorption of oral medications, reducing their effectiveness. It is advisable to take medications at least one hour before or four hours after consuming glucomannan to avoid potential interactions.
Research and Studies
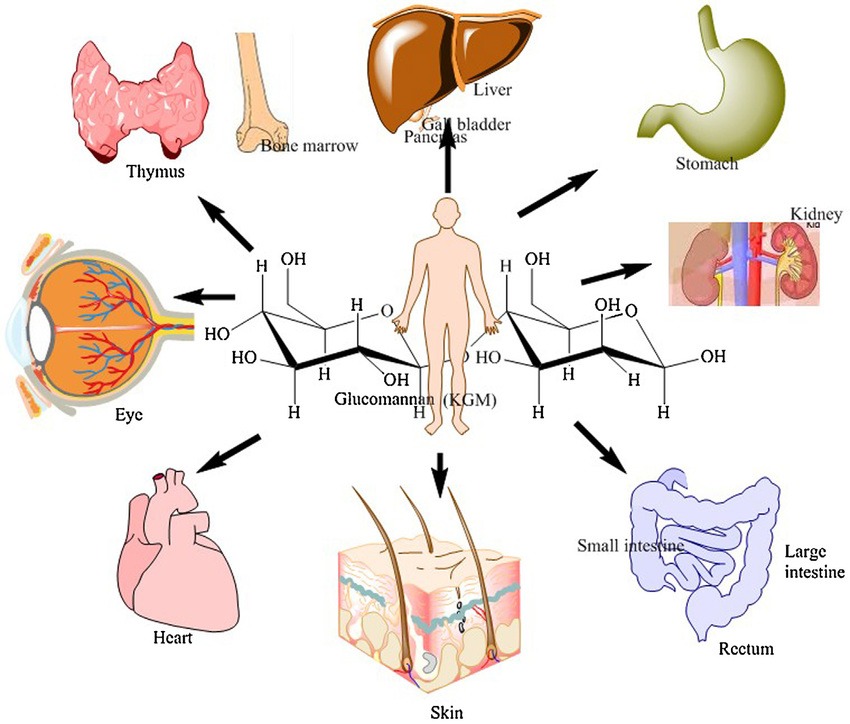
Overview of Key Scientific Studies on Glucomannan
Numerous scientific studies have explored the health benefits and effects of glucomannan, highlighting its potential in various health areas:
- Weight Loss: A study published in the Journal of Obesity investigated the effects of glucomannan on weight loss in overweight and obese participants. Over an 8-week period, those taking glucomannan experienced a significant reduction in body weight compared to the placebo group. Source
- Cholesterol Management: Research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition showed that glucomannan supplementation significantly reduced LDL cholesterol levels in participants, supporting its role in heart health. Source
- Blood Sugar Regulation: A study in the Diabetes Care journal found that glucomannan supplementation helped improve glycemic control in individuals with type 2 diabetes by reducing postprandial blood glucose levels. Source
- Digestive Health: The European Journal of Clinical Nutrition published findings indicating that glucomannan effectively alleviated constipation and improved bowel movement regularity in adults. Source
Summary of Findings and Evidence-Based Benefits
- Weight Loss and Appetite Control: Glucomannan helps promote weight loss by increasing satiety and reducing calorie intake. Its ability to form a gel-like substance in the stomach slows digestion and prolongs feelings of fullness.
- Cholesterol Management: Glucomannan has been shown to lower LDL cholesterol levels by binding to bile acids and promoting their excretion, thus reducing overall cholesterol levels in the blood.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: By slowing the absorption of carbohydrates, glucomannan helps stabilize blood sugar levels, making it beneficial for individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance.
- Digestive Health: As a soluble fiber, glucomannan aids in softening stools and promoting regular bowel movements, helping to alleviate constipation and improve overall digestive health.
- Gut Microbiome: Emerging research suggests that glucomannan may act as a prebiotic, supporting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria and contributing to a healthy gut microbiome.
Areas for Future Research
While existing studies have demonstrated the benefits of glucomannan, several areas warrant further investigation:
- Long-Term Effects: More long-term studies are needed to assess the sustained effects and safety of glucomannan supplementation over extended periods.
- Mechanisms of Action: Further research is required to fully understand the biochemical mechanisms through which glucomannan exerts its health benefits, particularly its effects on the gut microbiome and metabolic health.
- Population-Specific Effects: Studies focusing on different population groups, such as children, the elderly, and individuals with specific health conditions, would provide more comprehensive insights into the safety and efficacy of glucomannan.
- Combination Therapies: Research exploring the synergistic effects of glucomannan in combination with other dietary fibers or supplements could offer new therapeutic strategies for managing weight, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
- Gut Microbiome Impact: Further studies on how glucomannan influences the composition and function of the gut microbiome could provide deeper insights into its role in digestive health and systemic benefits.
